
Adageis is excited to announce the successful closure of our $2 million Seed round at the end of Q4 2024. This milestone marks a significant step forward in our mission to revolutionize healthcare technology and streamline operations for providers across the industry. Investing in the Future With this funding, we are strategically focusing on three key areas to drive growth and enhance our platform: 1. Upgrading Our Backend Infrastructure To better support the next generation of healthcare technology, we are investing in major backend improvements. These upgrades will enhance the scalability, speed, and reliability of our system, ensuring a seamless user experience for healthcare providers and administrators alike. 2. Expanding Our Sales Force To accelerate adoption and reach a broader audience, we are expanding our sales team. This investment will allow us to deploy rapid growth strategies, engage with more healthcare organizations, and demonstrate the value of Adageis’ solutions to providers looking to maximize efficiency and revenue. 3. Enhancing Connectivity with EHR Systems One of our top priorities is improving interoperability. We are enhancing our system’s connectivity to integrate with over 90 different Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. This will enable faster deployment and smoother integration for healthcare providers, ensuring they can seamlessly adopt and benefit from our platform. Looking Ahead The closing of our Seed round is just the beginning. As we continue to scale, our focus remains on delivering innovative solutions that empower healthcare professionals, optimize workflows, and improve patient care. We are excited for what’s ahead and look forward to sharing more updates as we advance on this journey. Stay tuned for more developments, and thank you to our investors, partners, and customers for your continued support!
In recent years, physician burnout has become a pressing concern in healthcare. With growing administrative burdens, particularly around documentation, many healthcare providers find themselves spending more time typing notes than caring for their patients. The result? Rising levels of stress, job dissatisfaction, and ultimately, burnout. But now, artificial intelligence (AI) offers a solution that can help The Burnout Crisis in Healthcare A 2023 Medscape survey revealed that 53% of physicians reported feelings of burnout , citing excessive administrative work as one of the leading causes. Healthcare professionals are spending an average of 16 minutes per patient completing electronic health records (EHRs), which can add up to several hours of documentation per day. For physicians who entered the field to provide compassionate care, this relentless data entry detracts from their core mission. The result is a growing number of providers feeling overwhelmed, emotionally drained, and distanced from their patients. Enter AI Scribe: The AI-Powered Solution AI technologies, like Adageis' new AI Scribe, are changing the game. By using advanced algorithms to assist in real-time note-taking and documentation, AI Scribe can drastically reduce the time physicians spend on charting. With an average note completion time of just 2 minutes, providers can refocus their energy where it matters most—on delivering quality care. By automating documentation tasks, AI Scribe doesn’t just save time—it also helps reduce the mental load of managing paperwork. Physicians no longer have to worry about facing hours of backlogged notes at the end of their day. Instead, AI Scribe works as a virtual assistant, capturing key information and structuring notes in the background, allowing providers to maintain eye contact and engage more meaningfully with their patients. AI as a Burnout Fighter The impact of tools like AI Scribe extends beyond just time savings. When physicians feel less overwhelmed by administrative tasks, they are less likely to experience burnout. They can focus on what they were trained to do—diagnose, treat, and connect with patients. This shift is crucial in an industry where human interaction and patient trust are essential to successful care. Physicians who have integrated AI into their practice have reported feeling a renewed sense of purpose and satisfaction. Being able to hand over repetitive tasks like note-taking frees them to concentrate on clinical decision-making and patient care. The Future of AI in Healthcare While AI isn’t a magic cure for all the challenges in healthcare, it is a powerful tool that can mitigate one of the most significant contributors to physician burnout: documentation overload. As AI continues to evolve, its role in supporting physicians will only grow, offering new ways to streamline workflows, enhance patient care, and protect the well-being of healthcare professionals. At Adageis, we believe that by empowering healthcare providers with innovative technology like AI Scribe, we can bring back the joy of practicing medicine. Physicians deserve tools that support—not hinder—their ability to provide care. With AI, we’re not just typing less; we’re caring more. ________________________________________ Ready to discover how AI Scribe can reduce burnout and improve your practice? Learn more and schedule a demo today

The shift towards value-based care has placed a premium on quality incentives. These incentives are designed to reward healthcare providers for delivering high-quality care, improving patient outcomes, and reducing costs. However, achieving and maximizing these incentives requires more than just good intentions—it demands a strategic approach rooted in data-driven decision-making. This is where data analytics comes into play. The Power of Data-Driven Decision-Making in Healthcare Data analytics has revolutionized various industries, and healthcare is no exception. In a field where decisions directly impact patient lives, the ability to harness and interpret vast amounts of data is invaluable. By leveraging data analytics, healthcare providers can: Identify Trends and Patterns: Data analytics enables the identification of trends and patterns in patient outcomes, treatment effectiveness, and operational efficiency. These insights allow providers to pinpoint areas for improvement, ensuring that resources are allocated where they can have the most significant impact. Predict Outcomes: Predictive analytics can forecast patient outcomes based on historical data, allowing healthcare providers to intervene proactively. For instance, by identifying patients at risk of readmission, providers can implement targeted interventions to prevent it, thereby improving quality scores. Optimize Resource Allocation: Efficient resource allocation is crucial in healthcare, where both human and financial resources are often limited. Data analytics can help optimize the use of these resources by identifying which areas require more attention and which practices yield the best results. Optimizing Quality Incentive Programs with Data Analytics Quality incentive programs, such as those under the Medicare Quality Payment Program (QPP), are designed to promote value-based care by rewarding providers who deliver high-quality care. However, these programs are complex, with numerous metrics and benchmarks to meet. This complexity can make it challenging for healthcare providers to fully capitalize on the incentives available to them. Our platform addresses this challenge by integrating advanced data analytics into the management of quality incentive programs. Here's how: Real-Time Performance Monitoring: Our platform provides real-time insights into performance across various quality metrics. By continuously monitoring these metrics, providers can make data-driven decisions to improve their performance, ensuring they meet or exceed the benchmarks required for maximum incentives. Digitizing your Contracts: We upload all your incentive rules into our AI-powered engine. Follow the Dollar: Included in the platform is your incentive reimbursement to help you see potential. Track where your revenue is coming from and identify areas where you could potentially increase earnings. The Future of Data Analytics in Healthcare As the healthcare industry continues to embrace value-based care, the role of data analytics will only grow. Future advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning promise to enhance the capabilities of data analytics even further, enabling more precise predictions, deeper insights, and more effective interventions. For healthcare providers, the ability to harness these tools is essential for staying competitive and maximizing quality incentives. Our platform is at the forefront of this movement, providing the analytics-driven insights needed to thrive in an increasingly data-driven healthcare environment. Data analytics is a necessity in healthcare today. By making data-driven decisions, healthcare providers can ensure they are delivering the highest quality care while also maximizing their financial rewards. Our ProActive platform is designed to empower providers with the insights they need to achieve these goals, positioning them for success in the era of value-based care.

The healthc are industry in the United States is undergoing a significant transformation as it continues its shift towards value-based care. This model, which emphasizes quality and outcomes over the volume of services provided, is designed to improve patient care while reducing costs. However, as promising as value-based care is, it comes with its own set of challenges that are placing financial pressure on healthcare providers. The Complex Landscape of Value-Based Care Value-based care is a critical focus for healthcare providers, but its implementation is far from straightforward. Several factors contribute to the complexity: 1. Physician Shortages: The U.S. is currently facing a shortage of physicians, which is projected to worsen in the coming years. This shortage puts additional strain on healthcare providers, who are already tasked with delivering high-quality care while managing a growing patient population. With fewer doctors available, maintaining the quality of care required under value-based care models becomes increasingly difficult. 2. Inefficiencies in Government Payer Systems: Government payers, such as Medicare and Medicaid, are integral to the value-based care framework. However, inefficiencies within these systems, including delayed payments and complex reimbursement processes, can hinder providers' ability to operate effectively. These challenges can lead to cash flow issues, making it harder for providers to invest in the resources necessary to succeed in a value-based care environment. 3. Dominance of Medicare Advantage: Medicare Advantage plans, which offer an alternative to traditional Medicare, have gained significant traction in the U.S. market. While these plans are a key component of the value-based care model, they also introduce additional layers of complexity. Providers must navigate varying reimbursement rates and performance metrics, which can add to the financial pressures they face. Balancing Quality and Costs with AI As healthcare providers grapple with these challenges, the need for innovative solutions has never been greater. One such solution is the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), into healthcare operations. Our platform's Patented AI Risk Engine is designed to help providers manage the dual pressures of improving quality and controlling costs. Here’s how: • Predictive Analytics for Patient Outcomes: The AI risk engine uses predictive analytics to forecast patient outcomes, allowing providers to identify at-risk patients early and intervene before costly complications arise. By proactively managing patient health, providers can reduce unnecessary hospitalizations and improve their performance on key quality metrics. • Optimized Resource Allocation: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify inefficiencies in care delivery. By optimizing resource allocation, providers can ensure that they are delivering the right care at the right time, reducing waste and improving patient outcomes. • Streamlined Reimbursement Processes: The AI risk engine can also assist in navigating the complex reimbursement landscape by automating claims submissions and ensuring that providers meet the specific requirements of different payer systems. This reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers and ensures faster, more accurate reimbursements. The Path Forward As value-based care becomes increasingly prevalent, healthcare providers must find ways to balance the demands of improving quality with the need to manage costs. The integration of AI-driven technologies, such as our Patented AI Risk Engine, offers a promising path forward. By leveraging these tools, providers can not only survive but thrive in a value-based care environment, ensuring that they deliver the highest quality care to their patients while maintaining financial stability. While the shift towards value-based care presents significant challenges, it also offers opportunities for innovation and improvement. Healthcare providers who embrace AI and other advanced technologies will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of this new landscape, ultimately leading to better outcomes for both patients and providers.

Women's health encompasses a wide range of care, from reproductive care to managing and preventing chronic illnesses. With our heavy loads of daily responsibilities, it's easy to neglect our health. However, prioritizing regular health screenings is one of the most important steps we can take for our long-term well-being. Understanding Women's Health Women’s health is unique and requires specialized surveillance. From puberty to menopause, women experience a range of hormonal changes that can impact overall health. Women are also at risk for specific health issues, such as breast and cervical cancer, osteoporosis, and reproductive health problems. Regular screenings are designed to monitor these unique aspects of women's health, ensuring early detection and intervention. Important Screenings for Women Breast Cancer Screening (Mammogram) Why It's Important: Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women. A mammogram can detect tumors that are too small to be felt, significantly improving the chances of successful treatment. Cervical Cancer Screening (Pap Smear and HPV Test) Why It's Important: Cervical cancer can often be prevented through early detection of precancerous changes. Regular Pap smears and HPV tests are crucial in catching these changes early. Bone Density Test (DEXA Scan) Why It's Important: Women are at higher risk for osteoporosis, especially after menopause. A DEXA scan measures bone density and can help prevent fractures by identifying early bone loss. Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Screening Why It's Important: Heart disease is a leading cause of death among women. Regular screenings for blood pressure and cholesterol levels help in managing heart health and preventing heart disease. Diabetes Screening Why It's Important: Type 2 diabetes is a growing concern, and women with a family history or other risk factors should be particularly vigilant. Early detection can prevent serious complications. Mental Health Screenings Why It's Important: Mental health is a crucial component of overall well-being. Screenings for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions can lead to timely support and treatment. Taking Charge of Your Health Our health is our most valuable asset. Regular health screenings are not just about detecting diseases; they’re about taking charge of our well-being. They provide a sense of empowerment, knowing that we are proactively managing our health. Women's health screenings offer early detection, preventive care, and peace of mind. Schedule your screenings, stay informed, and take control of your health. Remember, you are worth the time and effort it takes to ensure your health. Make that appointment today—because your health matters. Adageis is partnered with Ma’am Exams to support them in providing exceptional woman’s healthcare services to women in our community. Together, we’re committed to helping pr ovide proactive healthcare.

In today's healthcare, two primary approaches dominate the conversation: proactive healthcare and reactive healthcare. Understanding the distinction between these approaches and recognizing the benefits of proactive healthcare can significantly impact personal well-being and societal health outcomes. Proactive Healthcare: Prevention is Better than Cure Proactive healthcare emphasizes the prevention of illness and the promotion of overall well-being. This approach involves regular check-ups, screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle modifications to prevent diseases before they occur. The key components of proactive healthcare include: Routine Screenings and Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups and screenings help detect potential health issues early, allowing for timely intervention. Early detection of conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Vaccinations: Immunizations protect individuals from various infectious diseases, reducing the prevalence and spread of illnesses within communities. Vaccines are a cornerstone of preventive medicine, safeguarding both individual and public health. Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Encouraging healthy habits such as balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management can prevent chronic diseases and enhance overall quality of life. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in mitigating risk factors associated with heart disease, obesity, and mental health disorders. Education and Awareness: Providing individuals with knowledge about health risks and preventive measures empowers them to make informed decisions. Health education campaigns and community programs can raise awareness about the importance of proactive healthcare practices. Reactive Healthcare: Responding to Illness Reactive healthcare, in contrast, focuses on treating diseases and health conditions after they have developed. This approach involves diagnosing and managing illnesses through medical interventions, such as medications, surgeries, and therapies. While reactive healthcare is essential for addressing acute and chronic conditions, it often comes with higher costs and increased strain on healthcare systems. The Benefits of Proactive Healthcare Cost-Effectiveness: Preventive measures are generally more cost-effective than treating advanced diseases. Regular screenings and vaccinations can reduce the need for expensive treatments and hospitalizations, leading to significant healthcare savings for individuals and society. Improved Health Outcomes: Early detection and intervention can lead to better health outcomes. For instance, cancers diagnosed at an early stage are often more treatable and have higher survival rates compared to those detected at later stages. Proactive healthcare helps in managing chronic conditions more effectively, reducing the risk of complications and improving quality of life. Reduced Healthcare Burden: By preventing diseases and promoting overall well-being, proactive healthcare can alleviate the burden on healthcare systems. Fewer hospitalizations and medical interventions translate to reduced strain on healthcare resources, allowing for more efficient and equitable distribution of care. Enhanced Quality of Life: Proactive healthcare empowers individuals to take charge of their health, leading to enhanced physical, mental, and emotional well-being. A healthy lifestyle and preventive measures contribute to increased energy levels, better mood, and improved overall quality of life. Public Health Benefits: Widespread adoption of proactive healthcare practices can lead to healthier communities and reduced transmission of infectious diseases. Herd immunity through vaccinations, for example, protects vulnerable populations and contributes to the overall health of society. By prioritizing prevention, early detection, and healthy lifestyle choices, we can improve individual and public health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance overall quality of life. Embracing proactive healthcare empowers us to take control of our well-being and fosters a culture of health and wellness for generations to come.

The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have recently announced the ACO Primary Care Flex Model, a voluntary initiative aimed at enhancing primary care delivery within the Medicare Shared Savings Program (Shared Savings Program). Let’s delve into the details of this innovative model. What is the ACO Primary Care Flex Model? The ACO Primary Care Flex Model (ACO PC Flex Model) focuses on transforming primary care delivery through prospective payments and increased funding for primary care within Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs). By empowering participating ACOs and their primary care providers, the model aims to foster more innovative, team-based, person-centered, and proactive approaches to care. Key Objectives and Impact Health Outcomes and Quality Improvement: The ACO PC Flex Model seeks to improve health outcomes, enhance quality, and reduce costs of care. By emphasizing primary care, it aims to positively impact the health and well-being of Medicare beneficiaries. Growing ACO Participation: Starting from January 1, 2025, the model aims to increase ACO participation and expand the Shared Savings Program. It encourages more people with Medicare to engage in an accountable care relationship. Addressing Health Disparities: Improved funding for primary care can narrow health disparities, especially for underserved populations. The model incentivizes the development of new ACOs, particularly those supporting underserved communities. Application Process Organizations interested in participating must apply to the Shared Savings Program as either new ACOs or renewing ACOs by June 17, 2024. Applicant ACOs must also submit a supplemental ACO PC Flex application questionnaire by August 1, 2024. CMS plans to announce selected applicants in October 2024. Why Primary Care Matters Primary care serves as the foundation of a high-functioning health care system. Access to high-quality primary care leads to better health outcomes, preventive services, and coordinated care. However, workforce shortages and funding challenges persist. The ACO PC Flex Model aims to bridge this gap by prioritizing primary care within ACOs. The ACO Primary Care Flex Model represents a promising step toward improving primary care delivery and enhancing the well-being of Medicare beneficiaries. Organizations interested in participating should explore the Request for Applications (RFA) and consider how they can contribute to this transformative initiative. For more information, visit the CMS ACO Primary Care Flex Model page.
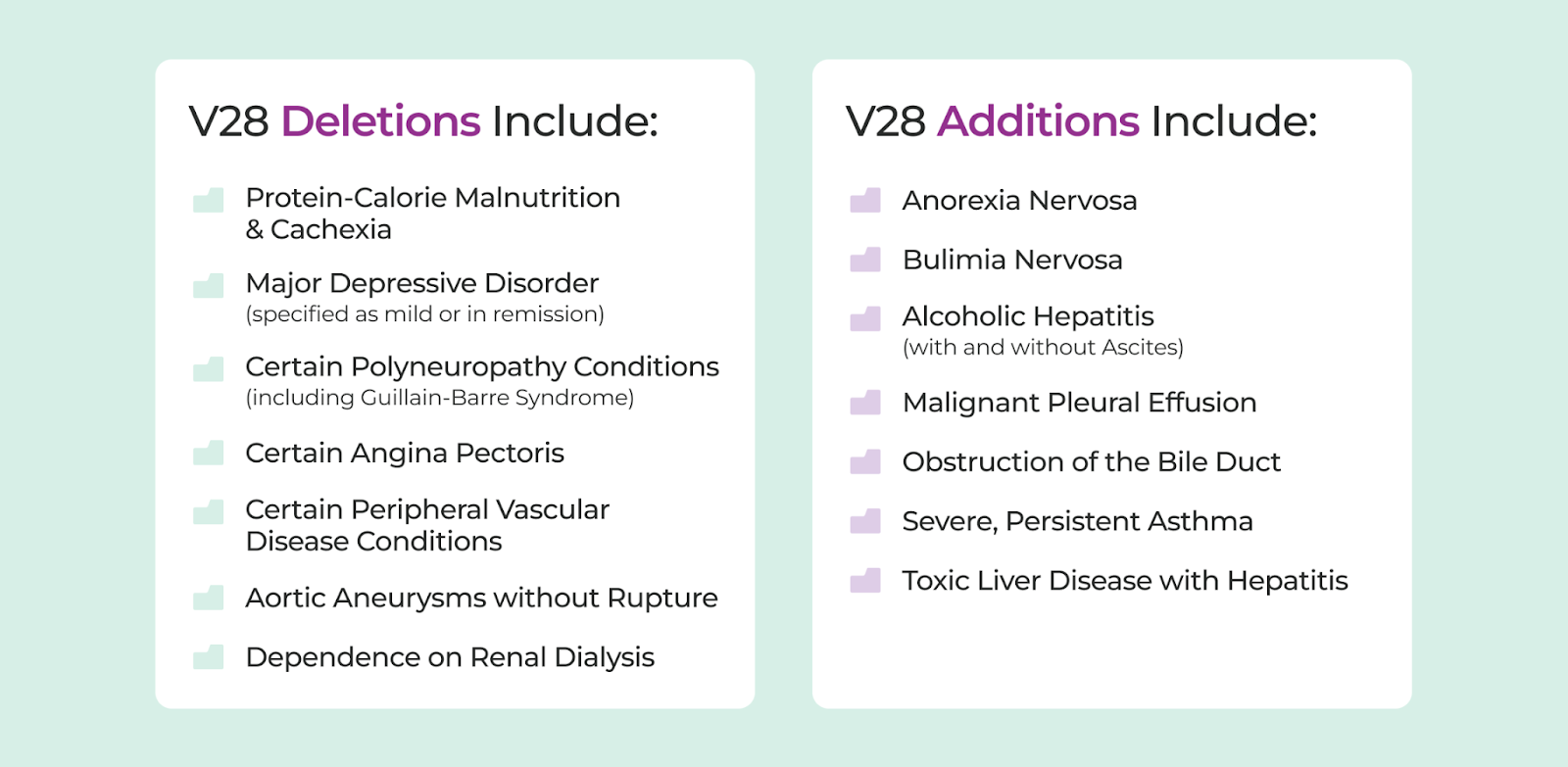
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has announced a transition to version 28 (V28) of the CMS-HCC model, a significant change in risk adjustment and patient population assessment for health plans. This shift, which will be gradually implemented over time and completed by 2025, requires health plans to adapt and strategize for financial sustainability, operational efficiency, and improved patient outcomes. The V28 model is more than just an update; it represents a new horizon in risk adjustment, with estimates suggesting that it will decrease Medicare Advantage risk scores by three percent to eight percent. This change has widespread implications for health plans, affecting revenue, care planning, and overall strategic direction. Key features of the V28 model include: New Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCCs): The V28 model refines HCCs to prioritize more severe or complex conditions, ensuring that health plans accurately assess and manage patient risk. Removal of ICD-10 codes: Over 2,000 ICD-10 codes will be removed from the current model, requiring health plans to identify and document every possible patient diagnosis to maximize risk scores and reimbursement rates. Updated coefficients and weights: Specific HCCs will have revised coefficients and weights, impacting risk scores and financial strategies. Transition Timeline and Importance of Early Adoption The transition to the V28 CMS-HCC risk adjustment model will occur in three stages: 2023: The V24 model carries significant weight with 67 percent, while the new V28 model holds a 33 percent share. 2024: The balance shifts, with 67 percent of the weight now assigned to the V28 model and only 33 percent to the V24 model. 2025: The transitio n is complete, with the V28 model taking center stage at 100 percent. Early adoption of the V28 model offers several advantages, including: Accuracy and compliance : Early adoption ensures that health plans are well-prepared to accurately assess risk, translating to better compliance with regulatory requirements and a reduced chance of compliance-related penalties. Strategic planning: Transitioning early allows health plans to proactively plan for the expected decrease in revenue and strategize for financial sustainability. Operational efficiency: A seamless transition minimizes operational disruptions, enabling health plans to focus on patient care and value-based partnerships without undue distractions. Competitive advantage: Early adopters gain a competitive edge by adapting to the new model's requirements and potentially outperforming competitors. Improved patient outcomes: Early transition facilitate s more accurate risk assessment of patient populations, leading to better patient care planning and improved health outcomes. Making the Transition Seamless To ensure a smooth transition to the V28 model, health plans should leverage a flexible analytics tool that can adapt to these new changes. Key features of such a tool include: Comprehensive V28 model analysis: The tool should provide a detailed analysis of how the V28 model impacts your organization, with actionable insights for strategic decision-making and risk adjustment optimization. Seamless transition: The analytics platform should be user-friendly and simplify the transition process, ensuring minimal disruption to current operations. Revenue optimization: The technology should maximize revenue capture under the V28 model, providing valuable insights into high-risk patients and areas of improvement. Enhanced risk management: The platform should enable better risk assessment and management, ultimately improving patient care and health plan sustainability. By investing in a flexible analytics tool, health plans can make the transition to the V28 model seamless, minimizing operational disruptions, and positioning themselves for success in the new healthcare landscape.

Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) have become a significant part of the healthcare landscape, with the goal of providing high-quality care to patients while managing costs. Medical practices interested in joining an ACO should understand the fundamentals, regulations, and strategies for selecting the right one. What is an ACO and its impact on medical practices? An ACO is a group of healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and other facilities, that work together to provide coordinated care to patients, particularly those with chronic conditions. ACOs aim to improve patient outcomes, reduce unnecessary tests and procedures, and lower healthcare costs. For medical practices, participating in an ACO can offer several benefits: Shared savings : ACOs that achieve cost savings while maintaining quality care can share the savings with participating providers. Improved care coordination: ACOs facilitate better communication and data sharing among providers, leading to more effective care plans and reduced duplication of services. Focus on value-based care: ACOs align with the broader shift from fee-for-service to value-based care models, which reward providers for delivering high-quality care and positive patient outcomes. Regulations and compliance considerations Medicare ACO programs, such as the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) and the Next Generation ACO Model, have specific regulations and requirements. Practices should be aware of the following: Patient attribution: ACOs are responsible for the care of assigned beneficiaries. Understanding patient attribution rules is crucial for accurate measurement of quality and cost performance. Quality measures: ACOs must report on specific quality metrics related to patient/caregiver experience, care coordination, and patient safety. Data sharing and reporting : Participating providers must share clinical and billing data with the ACO and comply with data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA. Strategies for choosing the right ACO When selecting an ACO, medical practices should consider the following factors: Alignment with practice goals : Ensure the ACO's objectives align with your practice's mission, vision, and values. Network of providers: Evaluate the ACO's network of providers to ensure access to necessary specialists and resources for your patient population. Financial model: Understand the ACO's financial structure, including risk levels, shared savings distributions, and fees. Data analytics and reporting : Assess the ACO's data analytics capabilities and reporting tools to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement. Culture and governance: Consider the ACO's leadership, decision-making processes, and commitment to transparency and collaboration. Joining an ACO can offer medical practices numerous benefits, including shared savings, improved care coordination, and alignment with value-based care models. However, understanding the fundamentals, regulations, and strategies for selecting the right ACO is crucial for success. By carefully evaluating ACO options based on practice goals, provider networks, financial models, data analytics, and culture, medical practices can make informed decisions and optimize their participation in these value-based care arr angements.
